What is MVC (Model View Controller) Architecture?
A Framework for Fullstack Web Developers
What is MVC?
MVC (or Model, View, Controller) Architecture is a framework for developing applications. It organizes the components of your web application and creates a separation of concerns. It makes a clear distinction between the frontend (what the user sees) and the backend (the data and logic) of your code. This makes it easier to work on large, complex applications and collaborate with other developers. This makes it possible to make changes without affecting areas of your code you don’t want to be altered.
To understand MVC, we need to understand the components of the framework.
(If you would like to watch my video explanation, here is my video on MVC ).
The Model:
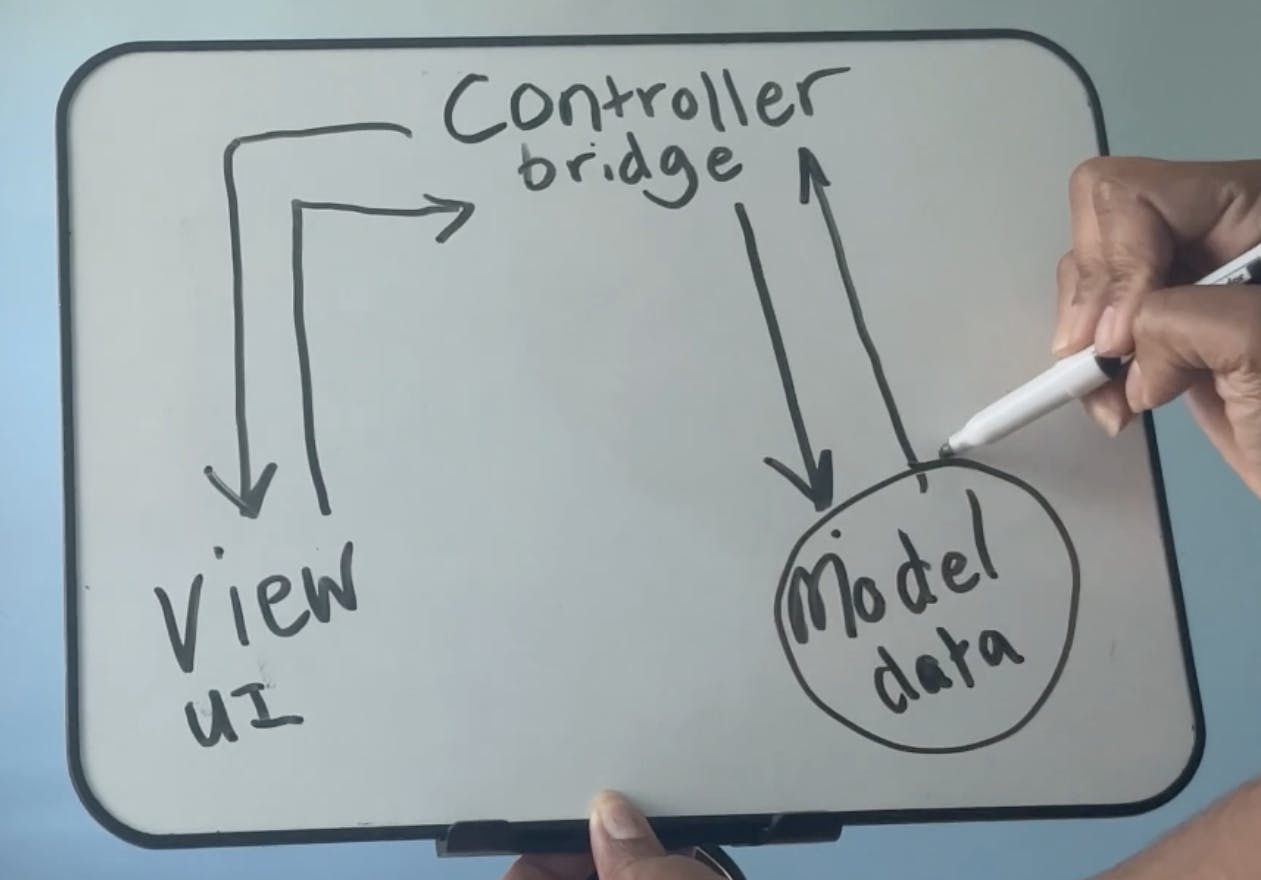
The model represents the data of your application. It is the manager that enforces the rules or logic of the application. It handles all of the updating, saving, and validation of data. It retrieves data like APIs, JSON objects, and databases, and sends them to the controller. When changes are made to its state, it updates the output to the controller which then sends it to the user to view and respond to.
The View:
The view represents the visual rendering of your data. It is the user interface that displays information that the user can interact with. The view does not manage data, it only shows it to the end user. It waits and responds to changes made in the model, then renders those changes on the screen.
The controller:
The controller is a bridge for data. It connects the Model with the View. It takes data supplied by the user interface and sends it to the model which then updates its database. It also takes data from the Model database and sends it to the View for the user to see. The Controller is also a decision maker. It sends commands to the model, decides what data to use, and handles requests from the user. It doesn't manage or handle data, it just gets it where it needs to go.
Pros and Cons of MVP:
Benefits of using MVC:
- For large web applications, dividing your code into 3 parts makes it easier to manage and find parts of the code to update and change
- Increases speed of development as developers can work on different parts of the application at the same time. One developer can work on the view, while the other works on the controller without affecting each other's work.
- It supports Asynchronous Method Invocation (AMI) which allows multiple operations to run at once, which increases the speed of the application
- It makes it easier to test the application due to the logic of layering the application in separate pieces, especially for large applications Increases SEO due to being able to specify parts of the application for optimized URLs.
Cons of MVC:
- Increases the complexity of the structure of your code which may make updating the application more involved
- Changes and updates may have to be done more frequently to maintain the site
- Developers have to be aware of the structure and technologies used for this framework
Overall, MVC is an important concept for developers to be aware of, as organizes our code in a structured way. While you may not have heard of the term “MVP”, as a developer you are probably already using some form of it to structure your applications.
Are you currently using MVC? If not, how do you organize your code?